Figure 1
Postero-anterior chest X-ray. There are huge lung air cysts, that occupy almost the whole left hemithorax. This chest X-ray belongs to a non-smoker male patient, who had dyspnoea on mild exertion.
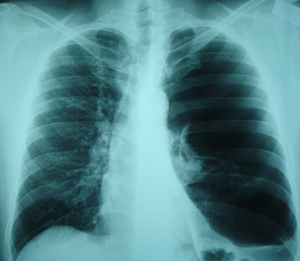
Figure 2a
Chest CT scan. An image at the level of the apical segments of the lungs. Huge lung air cysts are visible in the left hemithorax.

Figure 2b
Chest CT scan. Image at the level of the carina and the main bronchi. Again there are lung air cysts that occupy the left hemithorax.
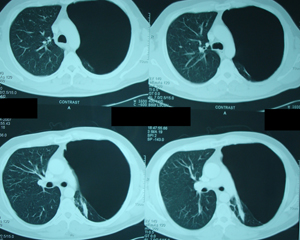
Figure 2c
Chest CT scan. Image at the level of the left lower pulmonary vein. The left hemithorax is occupied with lung air cysts, while a normal lung parenchyma is visible in small extent.

Figure 2d
Chest CT scan. Image superiorly to the diaphragm level. More lung parenchyma is
visible, while another large lung air cyst is still visible.
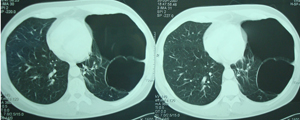
Figure 2e
Chest CT scan, at the level of the diaphragm. Mixed image, that shows normal lung
parenchyma and lung air cysts.
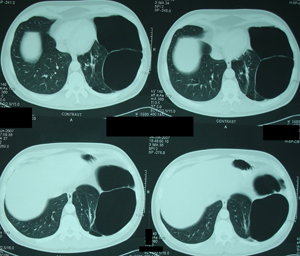
Figure 3a
Intraoperative photograph that shows the cyst wall, which seems to be quietly thick.
It was necessary to rupture the cyst because it was impossible to enter the
chest cavity, because of the huge cyst size and the trapped air, although the left lung
was occluded by the use of a double lumen tracheal tube.
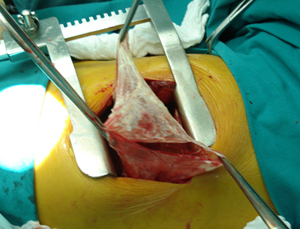
Figure 3b
Intraoperative photograph, which shows the suture line, which has been reinforced
by the use of Prolene 4/0. Also a tissue glue has been applied after the complete
expansion of the lung parenchyma.
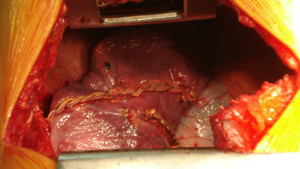
Figure 3c
Intraoperative photograph after the complete expansion of the lung lobes. The lung parenchyma seemed to be in an extremely good condition.
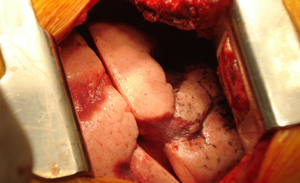
Figure 4a
A surgical specimen photograph, which represents a huge intact lung air cyst.
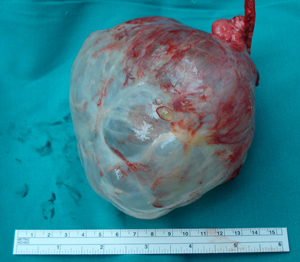
Figure 4b
Surgical specimen photograph, which represents the wall of the largest lung air cyst,
with a small segment of the lung parenchyma , which also has small cysts.
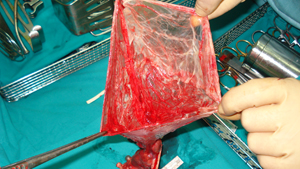
Figure 5
Postoperative postero-anterior chest X-ray, three days after the resection of the lung
air cysts. The two chest tubes are visible. There is complete expansion of the left
lung.
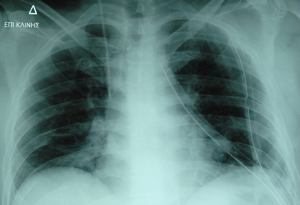
Figure 6
Postero-anterior Chest X-ray, six days before the patient being discharged from the
hospital. Complete expansion of the left lung, and the chest tubes have been removed.
Top